Vertical electrophoresis, or polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), is usually used to separate proteins, but it is also suitable for separating nucleic acids, or for visualising interactions between protein and DNA.
For the separation of proteins, the most common method is SDS-PAGE - here proteins are separated according to size by a denaturing system. In native PAGE, proteins are separated according to their natural charge and folding. Native PAGE is therefore also suitable for the analysis of protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions, or for high-resolution nucleic acid gels.

Preparation of PAGE gels
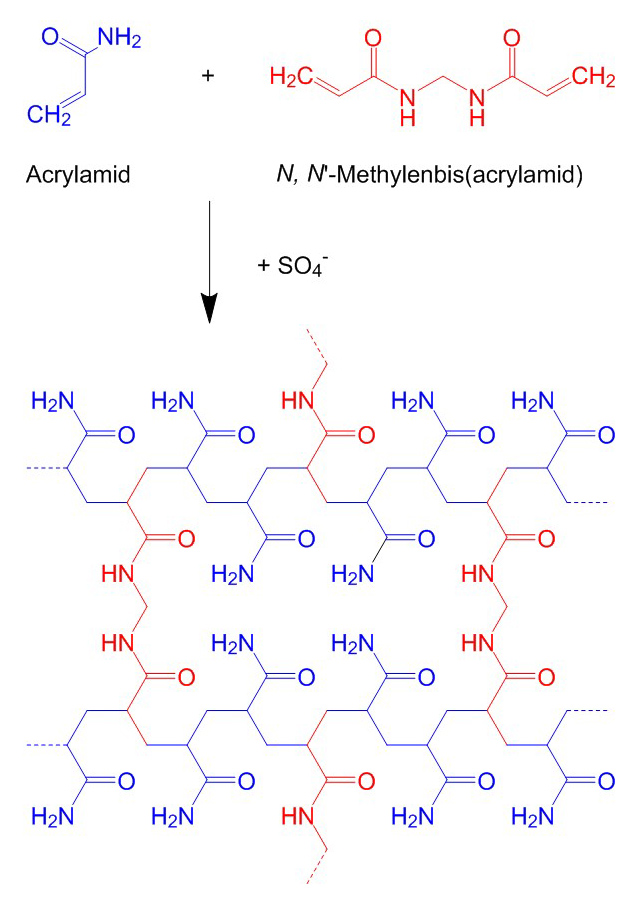
Polyacrylamide gels essentially consist of acrylamide and 2'-2'-methylenebisacrylamide, which are cross-linked by radical polymerisation. The acrylamide forms linear polyacrylamide chains which are cross-linked by the methylenebisacrylamide. The pore size of the gel is determined by the total concentration of acrylamide and bisacrylamide (% T), usually in a ratio of 29:1 to 37.5:1, and the concentration of bisacrylamide (% C). The higher the total concentration of acrylamide and bisacrylamide, the finer the pores of the gel. With regard to the bisacrylamide, a percentage of 5 % results in the smallest pores.
Further components needed for the preparation of a PAGE gel are an adequate buffer solution, usually SDS-PAGE/Lämmli buffer (separation of proteins) or TBE buffer (separation of nucleic acids), ammonium peroxodisulphate (APS) as radical initiator and tetramethylenediamine (TEMED) as polymerisation catalyst. The total concentration (% T) of acrylamide and bisacrylamide to produce a gel is usually 6-15%, depending on the size of the biomolecules to be separated.
In a commonly used form of protein electrophoresis, discontinuous SDS-PAGE, a two-phase gel is prepared. For this, two gel solutions with different concentrations and pH values are prepared - the gel solution with the higher concentration and a basic pH is poured first, it forms the running gel. The gel solution with the lower concentration and a neutral pH becomes the stacking gel. The samples are pipetted into the stacking gel and concentrate at the transition from the stacking gel to the finer-pored running gel. This optimises the gel run and the bands appear particularly sharp.
Acrylamide is a strong neurotoxin that can be absorbed through the skin as well as through the respiratory tract. To facilitate handling and reduce health risks, Carl Roth offers you a whole range of ready-to-use gel solutions and ready-to-use gels.
Further components needed for the preparation of a PAGE gel are an adequate buffer solution, usually SDS-PAGE/Lämmli buffer (separation of proteins) or TBE buffer (separation of nucleic acids), ammonium peroxodisulphate (APS) as radical initiator and tetramethylenediamine (TEMED) as polymerisation catalyst. The total concentration (% T) of acrylamide and bisacrylamide to produce a gel is usually 6-15%, depending on the size of the biomolecules to be separated.
In a commonly used form of protein electrophoresis, discontinuous SDS-PAGE, a two-phase gel is prepared. For this, two gel solutions with different concentrations and pH values are prepared - the gel solution with the higher concentration and a basic pH is poured first, it forms the running gel. The gel solution with the lower concentration and a neutral pH becomes the stacking gel. The samples are pipetted into the stacking gel and concentrate at the transition from the stacking gel to the finer-pored running gel. This optimises the gel run and the bands appear particularly sharp.
Acrylamide is a strong neurotoxin that can be absorbed through the skin as well as through the respiratory tract. To facilitate handling and reduce health risks, Carl Roth offers you a whole range of ready-to-use gel solutions and ready-to-use gels.
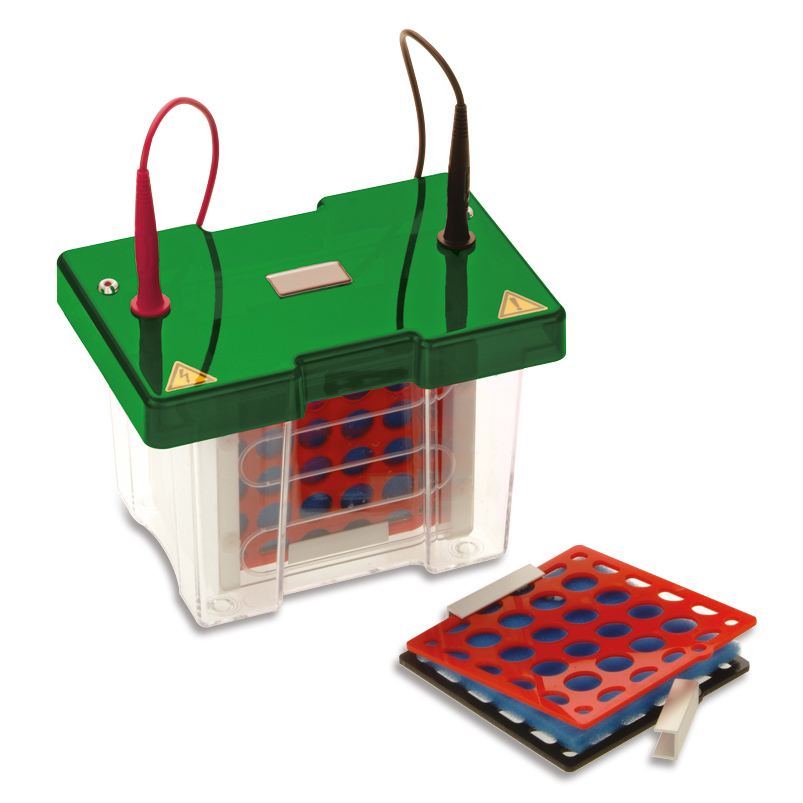
Vertical electrophoresis units and accessories
PAGE is performed in a vertical electrophoresis unit. To prepare the gel, two glass plates (one standard and one ear glass plate with a spacer in between) are placed against each other and clamped in a running module on a gel casting module. The ear glass plate is oriented inwards and the gel is poured between the glass plates. Once the gel has polymerised, the running module with the glass plates can be placed in a vertical unit and, after adding the running buffer and the samples, the gel run can be started.
Our chambers are available in three different sizes. The minimum scope of delivery includes an electrophoresis unit with buffer tank, safety lid and two cables, a running module with a practical fast-clamping mechanism, a cooling pad for gel cooling and a dummy plate. We have a wide range of accessories of combs, glass plates and spacers for each unit and all parts of the units can be purchased from us as spare parts.
Our chambers are available in three different sizes. The minimum scope of delivery includes an electrophoresis unit with buffer tank, safety lid and two cables, a running module with a practical fast-clamping mechanism, a cooling pad for gel cooling and a dummy plate. We have a wide range of accessories of combs, glass plates and spacers for each unit and all parts of the units can be purchased from us as spare parts.

Separation of biomolecules in PAGE
For the separation of biomolecules in PAGE, a running buffer is needed through which the current can flow, a loading dye that weighs down the sample and marks the running distance, and a ladder for size estimation.
When separating proteins in PAGE, the SDS-PAGE buffer according to Lämmli is usually used as the running buffer. SDS is an anionic surfactant that masks the intrinsic charge of the proteins and denatures them, thereby unfolding and linearising the proteins. In protein electrophoresis, the loading dye is used to protect and to prepare the sample. Most loading dyes also contain SDS or a comparable detergent. Some loading dyes have additional reducing properties and can thus dissolve resistant disulphide bonds. The protein ladders cover different size ranges and are acylated and prereduced.
For the separation of nucleic acids in PAGE, TBE buffer is usually used as a running buffer. The loading dyes contain different dye combinations and can be selected according to the fragment size to be separated. DNA ladders are available in different size ranges and for quantification also in equimolar distribution.
When separating proteins in PAGE, the SDS-PAGE buffer according to Lämmli is usually used as the running buffer. SDS is an anionic surfactant that masks the intrinsic charge of the proteins and denatures them, thereby unfolding and linearising the proteins. In protein electrophoresis, the loading dye is used to protect and to prepare the sample. Most loading dyes also contain SDS or a comparable detergent. Some loading dyes have additional reducing properties and can thus dissolve resistant disulphide bonds. The protein ladders cover different size ranges and are acylated and prereduced.
For the separation of nucleic acids in PAGE, TBE buffer is usually used as a running buffer. The loading dyes contain different dye combinations and can be selected according to the fragment size to be separated. DNA ladders are available in different size ranges and for quantification also in equimolar distribution.
Visualisation of biomolecules in PAGE gels
For the detection of proteins in PAGE, the gel is usually stained with Coomassie™ blue, as this dye binds to the basic side chains of amino acids and thus forms a stable complex with the proteins. With conventional Coomassie™ staining solutions, the gel background is also stained, which is why the gels first have to be de-stained with a methanol solution. Modern staining solutions with colloidal CoomassieTM are more sensitive and bind specifically to the proteins, which is why de-staining of the background is no longer necessary. As an alternative to Coomassie™ staining, proteins can be stained with a highly sensitive silver stain.
Nucleic acids can also be visualised in PAGE gels with a silver stain. This allows even the smallest amounts to be detected.
Nucleic acids can also be visualised in PAGE gels with a silver stain. This allows even the smallest amounts to be detected.
Extraction of biomolecules from PAGE gels
If biomolecules are to be purified or further investigated after PAGE, they must first be extracted from the gel. For this purpose, the relevant piece of gel is excised and can then be transferred to an elution tube, for example, in which it can be desalted and purified by dialysis and electroelution. The purified sample can then be concentrated by precipitation or ultrafiltration.

Transfer of proteins on membranes (Western blot)
For qualitative and specific detection of individual proteins or protein modifications, a Western blot can be performed after PAGE. For this purpose, the proteins must first be transferred from the gel to a suitable membrane, e.g. made of polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF), nitrocellulose (NC) or nylon. The transfer of the proteins to the membrane can be done either by electroblot or capillary transfer. For capillary transfer, blotting papers are needed which are placed over the membrane and under the gel. Capillary transfer can be performed either in a blotting tank or in a semi-dry blotter.
Power Supplies
For the generation of an electric field in the electrophoresis unit, a power supply is needed, which converts the electric current into the correct voltage. Our Power Supplies are available with different technical parameters, for the use of devices of different sizes, or for the connection of several units. Our Power Supplies are easy to use, are equipped with a timer with alarm function and have a high safety standard.
Technical support
Our product management provides you with product, application and scientific advice on technical questions regarding our range of chromatography and will help you find the right product for your application.Phone: +49 721 5606 - 513
e-Mail: chemicals@carlroth.de

Dr. Hacker